
Therapy Benefits: What Experts Say About The Gift of Therapy
The concept of the gift of therapy extends far beyond the traditional understanding of mental health treatment. Modern therapeutic practices have evolved into comprehensive wellness tools that address emotional, physical, and psychological well-being. Experts across multiple disciplines now recognize that therapy represents one of the most valuable investments individuals can make in their personal development and long-term health outcomes.
Research consistently demonstrates that therapeutic interventions produce measurable improvements in quality of life, emotional regulation, and overall resilience. Whether through psychological counseling, physical rehabilitation, or specialized treatment modalities, the benefits of therapy have become increasingly validated by scientific evidence and clinical experience. Understanding what experts say about these benefits can help individuals make informed decisions about their own wellness journeys.
The Science Behind Therapeutic Benefits
Contemporary neuroscience has provided compelling evidence that therapy creates measurable changes in brain structure and function. The American Psychological Association documents how therapeutic interventions alter neural pathways, reducing hyperactivity in stress-response regions while strengthening areas associated with emotional regulation and cognitive control.
Brain imaging studies reveal that individuals undergoing consistent therapeutic treatment show decreased activity in the amygdala—the brain region responsible for processing fear and anxiety. Simultaneously, increased activation occurs in the prefrontal cortex, which governs rational decision-making and emotional processing. This neurobiological shift represents the foundation of why therapy produces lasting psychological change rather than temporary relief.
Expert researchers emphasize that therapeutic resources and information increasingly demonstrate how talk therapy activates the same neural networks involved in learning and memory formation. This explains why therapeutic insights often produce transformative changes that persist long after treatment concludes. The brain essentially rewires itself through repeated exposure to new perspectives and coping strategies.
Longitudinal studies spanning decades show that individuals who engage in therapy maintain psychological improvements at significantly higher rates than those relying solely on medication. Research published in JAMA Psychiatry demonstrates sustained benefits for depression, anxiety, and trauma-related conditions when therapy forms the primary intervention.

Mental Health and Emotional Wellness
The most well-documented benefit of therapy involves its effectiveness for mental health conditions. Depression, anxiety disorders, post-traumatic stress, and other psychological challenges respond measurably to therapeutic intervention. Experts note that the gift of therapy lies partly in its ability to address root causes rather than merely managing symptoms.
Clinical psychologists emphasize that therapy provides tools for emotional regulation—the capacity to experience difficult emotions without becoming overwhelmed or reactive. Individuals learn to identify thought patterns that perpetuate emotional distress, then develop alternative cognitive frameworks that promote psychological resilience. This skill acquisition represents transformative change that extends throughout all life domains.
Anxiety disorders, which affect approximately 40 million American adults annually, respond particularly well to evidence-based therapeutic approaches. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), exposure therapy, and acceptance-commitment therapy all demonstrate efficacy rates between 60-80% for significant symptom reduction. Experts attribute these outcomes to therapy’s focus on addressing the cognitive and behavioral patterns maintaining anxiety.
Depression treatment through therapy shows comparable effectiveness to pharmaceutical interventions, with some studies indicating superior long-term outcomes. Therapists help individuals challenge the negative thought patterns and behavioral withdrawal that characterize depression, creating momentum toward psychological recovery. The collaborative nature of therapy also addresses the social isolation often accompanying depressive episodes.
Relationship difficulties and interpersonal conflicts benefit substantially from therapeutic intervention. Couples therapy improves communication patterns, increases emotional intimacy, and provides tools for conflict resolution. Family therapy addresses systemic patterns that perpetuate dysfunction across generations. These interventions prevent relationship dissolution while fostering deeper connection and understanding.
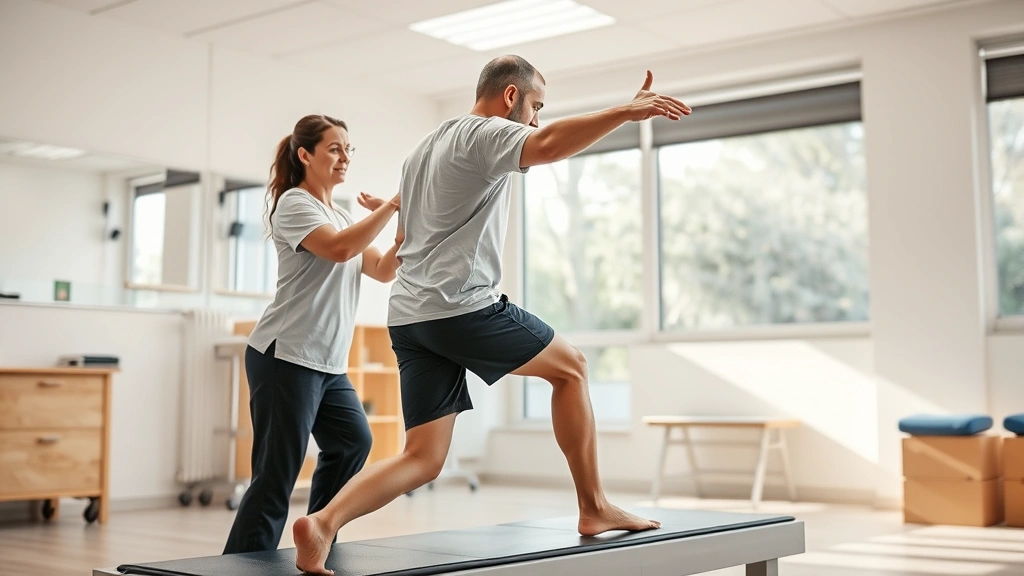
Physical Recovery and Rehabilitation
Beyond mental health, physical therapy represents another crucial dimension of therapeutic benefit. Experts in rehabilitation medicine emphasize that structured physical therapy accelerates recovery from injuries, surgeries, and chronic conditions. Physical therapy for children addresses developmental delays and movement disorders, setting foundations for lifelong physical capability.
Physical therapists work with patients to restore mobility, strength, and functional independence following traumatic injuries or surgical procedures. Evidence demonstrates that early intervention and consistent physical therapy reduce complications, accelerate healing, and improve long-term functional outcomes. Patients who engage actively in prescribed therapeutic exercises recover faster and achieve better results than those relying solely on medical intervention.
Chronic pain conditions—affecting millions of individuals globally—often respond more effectively to multimodal therapy than to pharmaceutical management alone. Physical therapy combined with cognitive-behavioral approaches helps individuals manage pain while maintaining functional capacity and quality of life. Experts recognize that addressing the physical, psychological, and social dimensions of pain produces superior outcomes.
Speech-language pathology represents another specialized therapeutic field with profound benefits. Speech therapy services address communication disorders, swallowing difficulties, and voice problems affecting children and adults. Individuals receiving speech therapy demonstrate measurable improvements in communication clarity, functional independence, and social participation.
Occupational therapy enhances daily functioning and independence for individuals with physical disabilities, neurological conditions, or developmental delays. Occupational therapy career opportunities have expanded as recognition grows regarding this field’s contribution to human functioning and quality of life. Occupational therapists help individuals adapt environments and develop strategies enabling participation in meaningful activities.
Specialized Therapy Modalities
Contemporary therapeutic practice extends far beyond traditional talk therapy, encompassing diverse modalities addressing different needs and preferences. Light therapy, including red light therapy services, demonstrates efficacy for seasonal affective disorder and certain dermatological conditions. These evidence-based modalities expand therapeutic options for individuals seeking alternative or complementary approaches.
Art therapy, music therapy, and movement-based therapies engage creative and embodied dimensions of healing. Research demonstrates that these modalities activate different neural pathways than talk therapy alone, providing benefits for trauma survivors, autism spectrum individuals, and those with limited verbal expression capacity. Experts increasingly recognize the value of multimodal therapeutic approaches.
Animal-assisted therapy shows remarkable benefits for anxiety, depression, and loneliness. The presence of therapeutic animals reduces cortisol levels, increases oxytocin production, and provides unconditional companionship that facilitates emotional opening. Veterans with PTSD, children with autism, and elderly individuals in care facilities all benefit measurably from animal-assisted therapeutic interventions.
Mindfulness-based therapies integrate meditation and acceptance practices into psychological treatment. Mindfulness-based stress reduction programs demonstrate efficacy for anxiety, chronic pain, and emotional dysregulation. These approaches teach individuals to observe thoughts and emotions without judgment, reducing their power to generate suffering.
Virtual reality therapy represents an emerging frontier in therapeutic innovation. Exposure therapy conducted through VR environments allows controlled, gradual confrontation of feared situations, proving particularly effective for phobias and PTSD. The immersive nature of VR therapy produces neurobiological responses comparable to real-world exposure while maintaining therapeutic safety parameters.
Long-Term Impact and Prevention
Experts emphasize that therapy’s benefits extend far beyond symptom reduction, fundamentally altering life trajectories through prevention and personal development. Individuals who engage in therapy develop psychological resilience—the capacity to navigate adversity without becoming derailed. This resilience protects against future mental health challenges and promotes sustained well-being.
Therapy functions as preventive medicine for psychological health. Individuals addressing trauma, developing healthy relationship patterns, and building emotional regulation skills substantially reduce their risk for future psychological disorders. The investment in therapy during periods of relative stability prevents the development of entrenched patterns that become increasingly difficult to address.
Children receiving therapy for emotional or behavioral challenges demonstrate improved academic performance, better peer relationships, and enhanced self-esteem. Early intervention prevents the crystallization of maladaptive patterns and provides developmental advantages extending throughout childhood and adolescence. Schools increasingly recognize therapy’s role in supporting student success.
Workplace productivity and professional relationships improve substantially when employees engage in therapy. Individuals addressing anxiety, depression, or interpersonal difficulties perform better, experience less burnout, and maintain healthier workplace relationships. Organizations increasingly support employee mental health through therapy coverage, recognizing the return on investment through improved productivity and reduced absenteeism.
Life satisfaction and subjective well-being show marked improvements in individuals receiving therapy. Beyond symptom reduction, therapy enables individuals to clarify values, develop authentic relationships, and pursue meaningful goals. This dimension of therapeutic benefit—enhanced life quality rather than merely reduced suffering—represents perhaps the most significant long-term impact.
Finding the Right Therapy for You
Selecting appropriate therapeutic intervention requires understanding personal needs, preferences, and the evidence supporting different modalities. Individuals benefit from researching therapists’ credentials, specializations, and therapeutic approaches. The therapeutic relationship itself constitutes a powerful component of healing—finding a compatible therapist significantly enhances treatment outcomes.
Different therapeutic approaches suit different individuals and presenting concerns. Cognitive-behavioral therapy excels for anxiety and depression, psychodynamic therapy addresses deep-seated patterns, and integrative approaches combine multiple modalities. Consulting with mental health professionals helps identify the most appropriate intervention for specific needs.
Location and accessibility influence therapy engagement. Finding therapy services near you removes barriers to consistent attendance. Teletherapy options expand access for individuals in rural areas or with transportation limitations. The proliferation of delivery modalities ensures that motivated individuals can access therapeutic support regardless of geographic location.
Financial considerations, while important, should not prevent individuals from accessing therapy. Many therapists offer sliding scale fees, community mental health centers provide affordable services, and insurance coverage increasingly includes therapy. Numerous organizations offer free or low-cost therapy to underserved populations. Cost concerns deserve discussion with potential therapists and mental health organizations.
Starting therapy represents a courageous commitment to personal growth and healing. Experts encourage individuals to approach the therapeutic process with openness and patience, recognizing that meaningful change typically unfolds gradually. The gift of therapy emerges through consistent engagement, vulnerability, and willingness to implement new perspectives and skills.
FAQ
What does research say about therapy effectiveness?
Extensive research demonstrates that therapy produces significant improvements in mental health outcomes, with effectiveness rates comparable to or exceeding medication alone for many conditions. Psychotherapy research journals consistently document sustained benefits extending years after treatment concludes, supporting therapy’s role as a primary intervention for psychological health.
How long does therapy typically take to show results?
Many individuals notice improvements within 4-6 weeks of consistent therapy, though more substantial changes typically emerge over several months. Complex issues may require longer-term therapeutic engagement. The timeline varies considerably based on presenting concerns, individual factors, and therapeutic approach. Discussing expected timelines with your therapist provides realistic expectations.
Can therapy be combined with medication?
Yes, combining therapy with appropriate medication often produces superior outcomes than either intervention alone. Mental health professionals can help determine whether medication, therapy, or combination treatment best serves individual needs. This integrative approach addresses both biological and psychological dimensions of mental health conditions.
Is therapy only for people with diagnosed mental illness?
Therapy benefits individuals across the spectrum of mental health, from those with clinical diagnoses to those seeking personal growth and life satisfaction. Many people without diagnosed disorders engage in therapy for relationship improvement, career transitions, or life challenges. The gift of therapy extends to anyone seeking enhanced well-being and personal development.
How do I know if I need therapy?
Indicators suggesting therapy might benefit you include persistent emotional distress, relationship difficulties, behavioral concerns, or significant life challenges affecting functioning. If you’re uncertain, consulting with a mental health professional provides clarity. Many therapists offer initial consultations to assess fit and discuss potential benefits for your specific situation.
What if I don’t connect with my first therapist?
The therapeutic relationship significantly influences outcomes, making compatibility important. If your first therapist isn’t the right fit, seeking another is entirely appropriate. Many individuals benefit from trying different therapists or modalities before finding the optimal match. Persistence in finding the right therapeutic fit substantially improves outcomes.


