Do Therapy Devices Aid Mindfulness? Expert Insights on Physical Therapy Devices
The intersection of physical therapy devices and mindfulness practices has become increasingly relevant in contemporary wellness discussions. As more individuals seek holistic approaches to health and mental well-being, the question of whether specialized devices can genuinely enhance mindfulness experiences deserves careful examination. Physical therapy devices range from simple tools like foam rollers and resistance bands to sophisticated technologies incorporating biofeedback, vibration therapy, and smart sensors that track movement patterns and physiological responses.
Mindfulness, fundamentally defined as present-moment awareness without judgment, has been extensively researched and validated by neuroscience. When combined with physical therapy interventions, these devices may create synergistic effects that amplify therapeutic benefits. Understanding this relationship requires exploring the mechanisms by which physical devices influence mental states, examining empirical evidence, and considering expert perspectives from both physical therapy and mindfulness meditation communities.

Understanding Physical Therapy Devices and Their Mechanisms
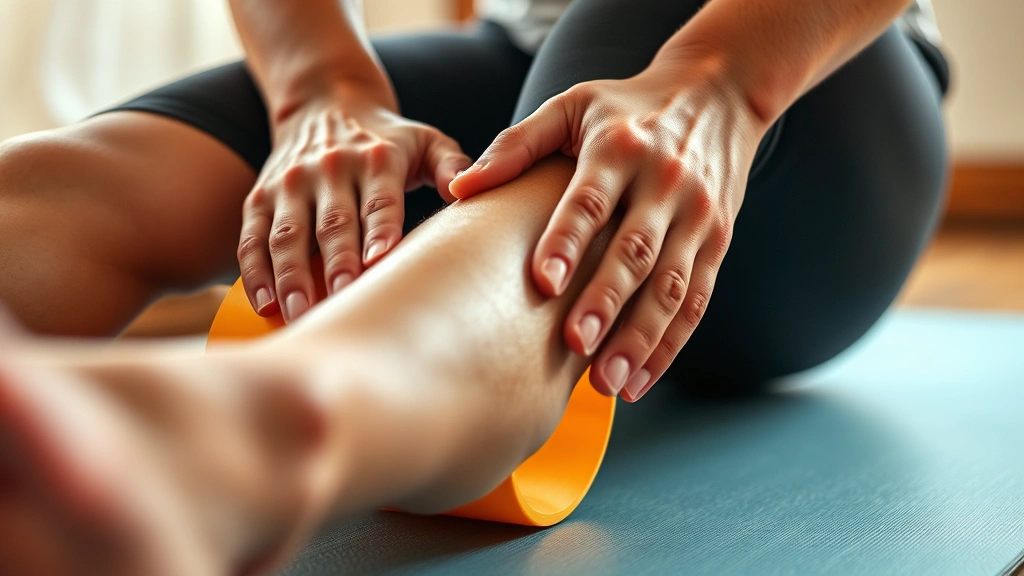
Physical therapy devices encompass a broad spectrum of tools designed to facilitate movement, reduce pain, improve mobility, and support rehabilitation. These instruments work through multiple mechanisms including mechanical stimulation, proprioceptive feedback, muscle activation patterns, and neurological pathway reinforcement. When exploring physical therapy cost considerations, many patients discover that investing in quality devices provides long-term value through consistent home-based therapy.
Modern physical therapy devices incorporate sophisticated technologies that provide immediate sensory feedback. Vibration plates, for instance, activate muscle fibers through rapid oscillations, creating proprioceptive awareness throughout the body. Resistance bands and suspension systems demand conscious engagement with movement mechanics. Wearable sensors and smart devices track metrics including range of motion, force distribution, balance, and coordination—data that practitioners and users can analyze to optimize movement patterns and build body awareness.
The psychological dimension of using physical therapy devices cannot be overlooked. The tactile feedback, quantifiable progress metrics, and structured guidance these tools provide create a sense of agency and control. This psychological component directly supports mindfulness development by anchoring attention to physical sensations and present-moment experiences. Users become acutely aware of muscle engagement, breathing patterns, and bodily responses during device-assisted therapy sessions.

The Science Behind Mindfulness and Body Awareness
Neuroscience research has demonstrated that mindfulness meditation produces measurable changes in brain structure and function, particularly in regions associated with attention, emotional regulation, and self-awareness. The anterior cingulate cortex, prefrontal cortex, and insula—areas critical for interoceptive awareness and present-moment focus—show increased activation and gray matter density in regular meditators. This neuroplasticity extends to enhanced proprioceptive processing, the body’s ability to sense its position and movement in space.
Body scan practices, a foundational mindfulness technique, deliberately cultivate interoceptive awareness by systematically directing attention through different body regions. This practice naturally aligns with physical therapy device usage, as both require focused attention on bodily sensations. Research published by the American Psychological Association indicates that embodied mindfulness practices—those integrating physical sensation with mental awareness—produce superior outcomes compared to attention-based meditation alone.
The vagus nerve, often called the “wandering nerve,” plays a crucial role in both physical relaxation and emotional regulation. Physical therapy devices that encourage gentle, rhythmic movement patterns activate the parasympathetic nervous system through vagal stimulation. This physiological shift creates an optimal internal state for mindfulness practice, reducing sympathetic arousal (fight-or-flight response) and facilitating the calm, receptive awareness characteristic of mindful states.
When individuals use physical therapy devices mindfully, they’re essentially training their nervous system to respond differently to physical sensation and movement. Rather than moving mechanically or reactively, they cultivate intentional, aware engagement with their bodies. This distinction transforms routine therapy sessions into comprehensive mind-body training experiences.
How Devices Enhance Mindful Movement Practice
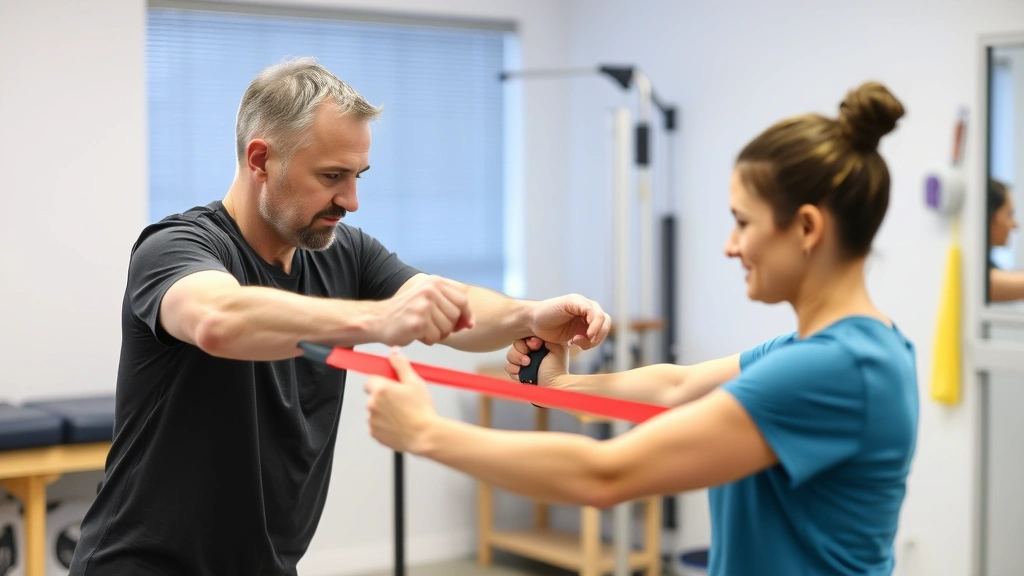
Mindful movement encompasses practices like yoga, tai chi, and qigong—disciplines that integrate physical practice with mental cultivation. Physical therapy devices enhance these practices by providing structural support, resistance, and feedback mechanisms that deepen awareness and improve biomechanical alignment. A foam roller, for example, becomes a mindfulness tool when used with deliberate attention to sensation rather than rushed self-massage.
Balance boards and stability devices demand heightened proprioceptive awareness. Users must continuously adjust micro-movements to maintain equilibrium, creating an intensely present mental state where wandering thoughts naturally diminish. This forced attention to the present moment mirrors meditation’s core mechanism while simultaneously building physical strength and coordination. The device essentially guides practitioners into mindfulness through the demands of safe, effective movement.
Resistance training equipment, when used with mindful intention, transforms into biofeedback devices. Feeling muscle engagement, controlling movement speed, and maintaining proper form require complete attentional engagement. Practitioners cannot simultaneously use resistance equipment and engage in distracted thinking—the physical demands naturally anchor consciousness in present-moment body awareness. This represents a practical advantage for individuals who struggle with traditional meditation but thrive with movement-based mindfulness.
Stretching and flexibility devices like yoga straps and blocks facilitate deeper body awareness by allowing practitioners to safely explore edge sensations and anatomical limitations. Rather than forcing stretches, mindful use of these devices encourages observation of resistance, sensation gradation, and the body’s subtle responses. This exploratory, non-judgmental approach perfectly embodies mindfulness principles while improving physical flexibility and mobility.
For individuals recovering from injury or managing chronic pain, physical therapy devices become particularly valuable for mindfulness integration. Pain conditions often fragment attention and create negative body relationships. Using devices mindfully allows practitioners to gradually rebuild positive associations with movement while maintaining focused, compassionate awareness of bodily sensations. This psychological reframing supports both physical recovery and emotional healing.
Biofeedback Technology and Real-Time Awareness
Contemporary biofeedback devices represent the technological frontier of mindfulness-device integration. These instruments measure physiological parameters—heart rate variability, skin conductance, muscle tension, breathing patterns, and brainwave activity—providing real-time data about internal states. Users can observe how their mental and emotional states directly influence physical responses, creating powerful learning experiences about mind-body interconnection.
Heart rate variability (HRV) biofeedback devices, for instance, guide users toward breathing patterns that optimize autonomic nervous system balance. By visualizing their HRV patterns on a screen and adjusting breathing to improve metrics, users develop concrete skills for activating parasympathetic responses—the physiological basis of relaxation and mindfulness states. This technology-assisted approach proves particularly effective for individuals who respond well to quantifiable feedback and measurable progress.
Wearable devices tracking movement quality and recovery metrics provide continuous feedback about physical state. This data accessibility supports mindfulness by making invisible physiological processes visible and analyzable. Users develop deeper understanding of how sleep, stress, activity levels, and emotional states interconnect and influence physical capacity. This systems-level awareness represents sophisticated mindfulness—understanding one’s complete psychophysiological ecosystem rather than isolated mental or physical components.
Virtual reality and augmented reality technologies create immersive environments for mindful movement practice. These systems can provide real-time form correction, adaptive difficulty, and motivational feedback while users perform therapy exercises. The immersive nature of VR naturally enhances present-moment focus, as the virtual environment demands complete attentional engagement. Research from Stanford’s Virtual Human Interaction Lab demonstrates that VR-based mindfulness interventions produce comparable results to traditional meditation.
Electromyography (EMG) devices, which measure muscle electrical activity, offer particularly valuable feedback for mindfulness practitioners learning to recognize and release tension patterns. By observing EMG readings, users develop real-time awareness of unconscious muscle contractions, enabling them to consciously relax specific muscle groups. This biofeedback loop accelerates learning of somatic awareness that might otherwise require months of traditional meditation practice.
Expert Recommendations for Device Integration
Physical therapists increasingly incorporate mindfulness principles into rehabilitation protocols, recognizing that conscious, aware movement produces superior outcomes compared to mechanical exercise. The American Physical Therapy Association acknowledges embodied cognition—the principle that physical experience shapes mental and emotional states—as foundational to modern therapeutic practice. Experts recommend selecting devices that match individual preferences and physical capacities rather than pursuing trendy options.
Mental health professionals and mindfulness teachers emphasize that devices should support rather than replace direct awareness training. A device used mechanically without mindful attention provides physical benefits but misses psychological and neurological advantages of integrated practice. The optimal approach combines device usage with conscious attention, breathing awareness, and the non-judgmental observation characteristic of mindfulness meditation. Consulting therapy resources and information can help individuals understand how to combine these approaches effectively.
Experts recommend starting with simple devices that provide clear sensory feedback without overwhelming complexity. Foam rollers, resistance bands, and balance boards offer excellent entry points because they provide immediate tactile sensation without technological learning curves. As practitioners develop comfort integrating mindfulness with device usage, they can progress toward more sophisticated biofeedback and measurement technologies.
The importance of proper instruction cannot be overstated. Even simple devices require correct usage to prevent injury and maximize effectiveness. Professional guidance from physical therapists ensures that device selection aligns with individual rehabilitation goals, physical limitations, and mindfulness capacities. Many practitioners benefit from structured programs combining professional guidance with independent home practice using devices.
Research from the National Center for Biotechnology Information demonstrates that consistency matters more than intensity. Regular, mindful device usage produces superior outcomes compared to occasional intensive sessions. Experts recommend establishing sustainable routines that feel manageable and enjoyable, recognizing that habit formation and intrinsic motivation support long-term practice adherence.
Practical Applications and Case Studies
Clinical evidence increasingly supports device-assisted mindfulness interventions for various populations. Individuals recovering from orthopedic surgery often experience anxiety and fear-avoidance around movement. Introducing physical therapy devices within a mindfulness framework helps patients gradually rebuild confidence and body awareness while managing pain and emotional responses. The combination of structural support (device) and mental training (mindfulness) produces faster, more complete recovery.
Chronic pain patients represent another population benefiting significantly from integrated device-mindfulness approaches. Pain conditions create habitual tension patterns and negative body relationships. Using physical therapy devices mindfully—exploring sensation without judgment, gradually building strength, and developing positive movement associations—helps break maladaptive patterns. Patients report improved pain management, reduced medication dependence, and enhanced quality of life through this integrated approach.
Athletes increasingly use biofeedback devices and smart equipment to optimize performance through mindfulness-informed training. Real-time feedback about muscle activation, movement efficiency, and stress responses enables athletes to develop body awareness that translates into improved technique, injury prevention, and mental resilience. Elite sports programs now routinely integrate biofeedback technology with mindfulness coaching.
Individuals managing anxiety disorders benefit from device-assisted proprioceptive grounding. When anxiety creates dissociation and disconnection from physical sensations, using therapy devices with focused attention anchors consciousness in the body. The tactile feedback and movement demands naturally interrupt anxious thought patterns while building confidence in physical capacity. This grounding mechanism provides practical anxiety management tools that complement traditional psychological interventions.
Older adults using physical therapy devices within mindfulness frameworks show improved balance, reduced fall risk, and enhanced cognitive function. The combination of physical exercise (device usage) and cognitive training (mindfulness attention) produces synergistic neurological benefits. Additionally, the social and purposeful nature of structured device-based practice programs supports emotional well-being and life satisfaction in aging populations.
For individuals exploring occupational therapy career paths, understanding device-mindfulness integration represents an emerging specialization. Forward-thinking practitioners are developing innovative programs that combine therapeutic devices with mindfulness training, creating comprehensive interventions that address physical, cognitive, and emotional dimensions of health. This integrated approach increasingly defines best practices in rehabilitation and wellness.
Complementary wellness modalities also benefit from device integration. Individuals exploring red light therapy options often combine these interventions with physical therapy devices for enhanced recovery. The synergistic effects of multiple modalities—light therapy supporting cellular recovery while physical therapy devices build strength and mindfulness anchors present-moment awareness—create comprehensive healing approaches addressing multiple physiological systems simultaneously.
FAQ
Can physical therapy devices replace traditional mindfulness meditation?
Physical therapy devices represent valuable supplements to meditation but not direct replacements. While device-assisted movement naturally cultivates present-moment awareness, traditional meditation develops specific attentional and emotional regulation capacities that physical practice alone may not fully address. The most comprehensive approach combines both modalities, using devices for embodied awareness while maintaining dedicated meditation practice for mental training.
What devices offer the best mindfulness benefits for beginners?
Simple devices providing clear sensory feedback work best initially: foam rollers, resistance bands, balance boards, and yoga props. These tools require minimal learning curves while providing immediate proprioceptive awareness. As practitioners develop comfort integrating mindfulness with movement, they can progress toward more sophisticated biofeedback devices and smart equipment that measure physiological parameters.
How long before experiencing mindfulness benefits from device usage?
Individuals typically notice improved body awareness within 1-2 weeks of consistent, mindful device practice. More substantial benefits—reduced anxiety, improved emotional regulation, enhanced pain management—generally emerge after 4-8 weeks of regular practice. As with traditional meditation, consistency matters more than duration; daily 15-20 minute sessions prove more effective than occasional longer sessions.
Are biofeedback devices necessary for device-assisted mindfulness?
Biofeedback devices enhance learning and provide motivating metrics but aren’t essential for developing mindfulness through physical practice. Many individuals cultivate profound body awareness using simple, non-technological devices combined with conscious attention. Biofeedback technologies primarily accelerate learning and appeal to individuals who respond well to quantifiable feedback and data-driven approaches.
Can device-assisted mindfulness help with anxiety and stress?
Yes, research demonstrates significant anxiety and stress reduction through integrated device-mindfulness practice. The physical activity component activates parasympathetic responses, while mindfulness attention prevents anxious thought spirals. The combination proves particularly effective because it addresses both physiological arousal and mental patterns simultaneously. Understanding therapy cost information helps individuals determine whether professional guidance would support their anxiety management goals.
What’s the relationship between device usage and pain management?
Physical therapy devices reduce pain through multiple mechanisms: strengthening supporting muscles, improving movement patterns, and reducing protective tension. Adding mindfulness to this process further reduces pain perception by changing the relationship to sensation and reducing fear-avoidance behaviors. Research shows that mindful device usage produces superior pain outcomes compared to mechanical exercise alone.