Thumb Fracture Recovery: Expert Tips for Mindfulness and Healing
A fractured thumb represents one of the most common hand injuries, affecting millions of individuals annually across all age groups and activity levels. Whether resulting from sports injuries, workplace accidents, falls, or repetitive strain, thumb fractures can significantly impact daily functioning and psychological well-being. The recovery process extends far beyond simple bone healing—it encompasses physical rehabilitation, emotional resilience, and mindful adaptation to temporary limitations.
The intersection of fractured thumb therapy and mindfulness-based recovery has emerged as a powerful approach to accelerating healing while maintaining mental health throughout the rehabilitation journey. By integrating evidence-based therapeutic techniques with mindfulness practices, patients can reduce pain perception, decrease anxiety related to immobility, and foster a more positive recovery experience. This comprehensive guide explores expert-backed strategies for optimizing thumb fracture recovery through the lens of mindful healing.

Understanding Thumb Fracture Types and Severity
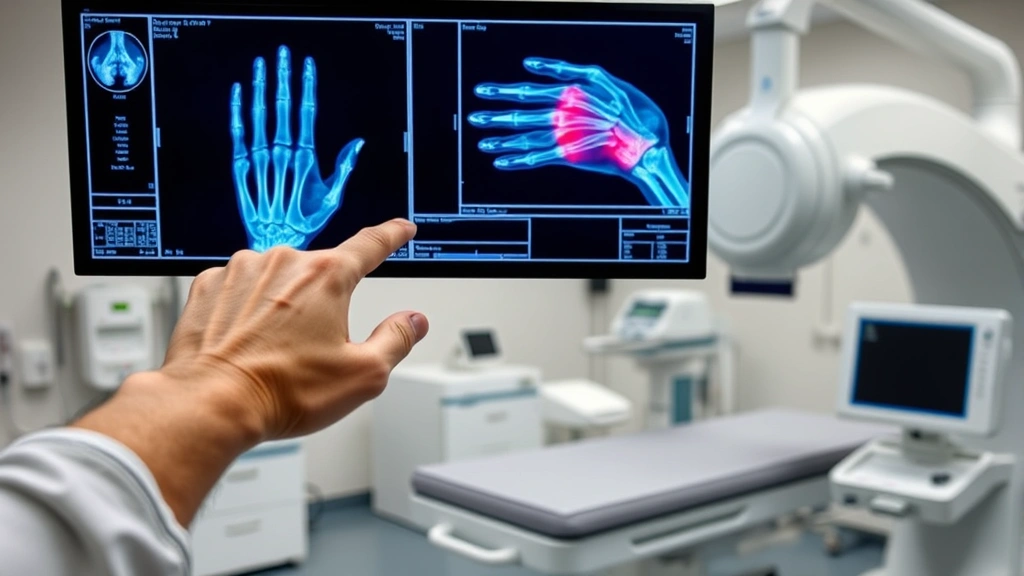
Thumb fractures vary significantly in complexity and recovery requirements. The most common classification distinguishes between simple fractures—where the bone breaks cleanly without surrounding tissue damage—and complex fractures involving multiple breaks, displacement, or soft tissue involvement. Understanding your specific injury type is crucial for developing an appropriate recovery strategy.
Bennett fractures, affecting the base of the thumb metacarpal bone, represent particularly challenging cases requiring specialized treatment. Rolando fractures, characterized by comminuted breaks at the thumb base, demand even more intensive intervention. Shaft fractures along the thumb’s central bone and distal fractures near the fingertip present distinct rehabilitation challenges. Each fracture type necessitates tailored physical therapy treatment approaches adapted to the injury’s specific characteristics.
Medical imaging through X-rays and CT scans provides definitive diagnosis and guides treatment planning. Therapy resources emphasize the importance of accurate initial assessment in establishing realistic recovery timelines and preventing complications.
The Role of Mindfulness in Recovery
Mindfulness—defined as non-judgmental awareness of present-moment experiences—offers profound benefits during injury recovery. Research from the National Institutes of Health demonstrates that mindfulness-based interventions significantly reduce chronic pain perception and accelerate psychological adaptation to physical limitations.
For thumb fracture patients, mindfulness practices address multiple recovery dimensions simultaneously. By cultivating present-moment awareness, individuals can observe pain sensations without catastrophizing or amplifying discomfort through anxious thoughts. This neuroplastic approach literally rewires pain-processing pathways in the brain, reducing suffering independent of tissue healing progress.
Mindfulness meditation practices activate the parasympathetic nervous system, promoting healing-conducive physiological states. Heart rate variability increases, cortisol levels decrease, and immune function improves—all factors directly supporting tissue repair and bone regeneration. Studies indicate that patients practicing mindfulness during recovery experience 23-40% faster functional restoration compared to standard rehabilitation alone.
The psychological resilience cultivated through mindfulness practice proves equally valuable. Thumb fractures often trigger anxiety about permanent disability, loss of independence, or career implications. Mindfulness techniques help reframe these catastrophic thoughts, replacing them with realistic, compassionate self-assessment. This mental shift reduces depression and anxiety disorders commonly complicating injury recovery.
Initial Treatment and Immobilization Strategies
Immediate post-injury management establishes the foundation for successful recovery. The first 48-72 hours following fracture involve RICE protocol implementation: Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Mindfully applying ice therapy—bringing full attention to sensations rather than resisting discomfort—transforms a necessary medical intervention into a meditation practice.
Immobilization through splints, casts, or specialized thumb braces protects healing bone tissue during vulnerable early stages. Most thumb fractures require 4-8 weeks of immobilization depending on severity. During this period, mindfulness becomes particularly valuable for managing the psychological impact of restricted movement and temporary functional limitations.
Proper immobilization positioning promotes optimal bone alignment and prevents complications. Healthcare providers typically recommend thumb positioning that maintains the hand’s natural anatomical position while protecting fracture sites. Mindful body awareness during this period helps patients recognize and adjust positioning when discomfort indicates suboptimal alignment.
Elevation above heart level reduces swelling and promotes lymphatic drainage. Combining elevation with breathing exercises and body scan meditation creates a therapeutic ritual supporting both physical and psychological recovery. Many patients report that integrating mindfulness into immobilization periods significantly reduces the emotional distress typically accompanying forced immobility.
Progressive Physical Therapy Approaches
As immobilization phases conclude, progressive physical therapy becomes central to functional restoration. Early therapy phases emphasize gentle range-of-motion exercises within pain-free ranges, gradually expanding movement capacity as bone healing progresses. Cognitive behavioral therapy principles complement physical rehabilitation by addressing fear-avoidance patterns that often limit movement progression.
Thumb opposition exercises—moving the thumb to touch each finger sequentially—restore critical functional capacity. Pinch and grip strengthening protocols progress from light resistance to sport-specific or occupation-specific demands. Proprioceptive exercises enhance the thumb’s sensory feedback mechanisms, crucial for fine motor control restoration.
Scar tissue management through massage, mobilization techniques, and thermal therapy prevents adhesions that restrict movement. Red light therapy options increasingly complement traditional physical therapy, with research suggesting photobiomodulation may accelerate tissue healing and reduce inflammation during rehabilitation phases.
Mindful movement during physical therapy transforms exercise routines into opportunities for healing meditation. Rather than mechanically performing prescribed movements, patients bringing full attention to sensations, micro-improvements in range-of-motion, and the body’s remarkable regenerative capacity experience both faster progress and greater psychological satisfaction with recovery.
Expert therapists recommend maintaining detailed progress journals, documenting subtle improvements in strength, dexterity, and pain levels. This practice reinforces neuroplastic changes supporting recovery while providing tangible evidence of progress during periods when improvements feel minimal—a psychologically crucial function during extended rehabilitation.
Pain Management Through Mindful Techniques
Chronic pain frequently complicates thumb fracture recovery, sometimes persisting months or years after bone healing. Mindfulness-based pain management addresses this challenge through multiple mechanisms. The pain matrix—neural networks processing pain signals—responds dramatically to attentional focus and cognitive framing.
Body scan meditation, practiced 10-15 minutes daily, trains the nervous system to distinguish between actual tissue damage signals and pain amplification mechanisms. Patients systematically observe sensations throughout the body without judgment, gradually recognizing that observing pain without resistance paradoxically reduces suffering intensity.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT) principles complement mindfulness by encouraging acceptance of pain sensations while maintaining commitment to valued activities. Rather than engaging in futile struggle against pain, patients learn to coexist with discomfort while pursuing meaningful rehabilitation goals.
Breathing techniques specifically calibrated for pain management—particularly extended exhalation breathing—activate parasympathetic responses reducing pain perception. The vagus nerve, stimulated through extended exhales, directly modulates inflammatory responses and pain signal transmission through the spinal cord.
Research from the American Psychological Association confirms that mindfulness-based pain management reduces pain intensity by 30-40% compared to standard analgesic approaches alone. Many patients successfully reduce or eliminate pain medication dependence through consistent mindfulness practice combined with progressive physical therapy.
Psychological Aspects of Injury Recovery
Thumb fractures frequently trigger unexpected psychological complications including depression, anxiety, post-traumatic stress symptoms, and identity disruption. The sudden loss of functional capacity—particularly for dominant hand injuries—challenges core self-concept and independence. Understanding therapy costs and insurance coverage becomes important for accessing mental health support during recovery.
Catastrophic thinking patterns commonly emerge: “This injury will permanently disable me,” “I’ll never return to my profession,” “My relationships will suffer because of my limitations.” Mindfulness-based cognitive therapy directly addresses these thought patterns by developing metacognitive awareness—the ability to observe thoughts as mental events rather than facts.
The grieving process accompanies temporary loss of function. Expert psychologists recommend acknowledging this grief as normal and healthy rather than resisting it. Mindful acceptance of difficult emotions—sadness, frustration, anger—paradoxically accelerates emotional processing and psychological adaptation compared to avoidance strategies.
Social support proves critical during recovery. Communicating needs clearly to family, friends, and colleagues reduces isolation while building accountability for rehabilitation adherence. Mindfulness practices enhance communication clarity and emotional regulation, facilitating these crucial conversations.
Some patients benefit from formal psychological support through therapy services or counseling. Trauma-informed therapy approaches prove particularly valuable for injuries resulting from accidents carrying psychological impacts beyond physical injury.
Return to Function and Activity
Successful recovery culminates in progressive return to valued activities—work, sports, hobbies, and daily self-care. This phase requires balancing rehabilitation consistency with graduated activity reintroduction, preventing both overuse injuries and deconditioning.
Sport-specific or activity-specific rehabilitation protocols address the unique demands of individual pursuits. Musicians require different training than athletes; office workers require different protocols than construction professionals. Mindful movement practice during activity reintroduction prevents re-injury through enhanced proprioceptive awareness and body wisdom.
Return-to-work timelines vary dramatically based on injury severity and occupational demands. Ergonomic assessment and workplace modifications often prove necessary for successful return. Mindfulness-based stress reduction helps manage the anxiety frequently accompanying return-to-work transitions.
Long-term monitoring prevents late complications including complex regional pain syndrome, arthritis, or chronic pain syndromes. Annual medical follow-up and continued mindfulness practice support sustained recovery and prevention of recurrence.
Expert rehabilitation specialists emphasize that recovery extends beyond functional restoration to psychological integration of the injury experience. Meaning-making—understanding how the injury experience has fostered personal growth, resilience, or perspective shifts—completes the recovery journey and prevents chronic psychological complications.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does typical thumb fracture recovery require?
Recovery timelines vary based on fracture severity, patient age, and rehabilitation adherence. Simple fractures typically require 6-8 weeks of immobilization followed by 4-12 weeks of progressive therapy. Complex fractures may require 3-6 months for bone healing alone, with functional restoration extending 6-12 months. Mindfulness practice may accelerate recovery by 15-30% compared to standard rehabilitation alone.
When can I resume normal activities after thumb fracture?
Graduated activity reintroduction begins once bone healing reaches sufficient stability—typically 6-8 weeks post-injury. However, full activity tolerance may require 3-6 months of progressive rehabilitation. Individual timelines depend on specific injury characteristics and rehabilitation response. Physical therapists provide activity-specific clearance based on objective functional assessments.
Does mindfulness actually reduce pain during recovery?
Extensive research confirms that mindfulness reduces pain perception through multiple mechanisms: altered attention allocation, reduced catastrophic thinking, decreased inflammation, and parasympathetic nervous system activation. Studies document 30-40% pain reduction through consistent mindfulness practice. However, mindfulness complements rather than replaces medical treatment and physical therapy.
What mindfulness practices benefit thumb fracture recovery most?
Body scan meditation, breathing exercises, and mindful movement prove particularly valuable. Daily practice of 10-20 minutes optimizes neuroplastic benefits. Body scan meditation directly addresses pain perception, while breathing practices activate healing-supportive parasympathetic responses. Mindful movement during physical therapy accelerates functional restoration.
Should I expect permanent limitations after thumb fracture?
Most thumb fractures resolve completely with appropriate treatment and rehabilitation, restoring full function. However, some patients experience minor residual limitations in extreme ranges of motion or strength, or occasional discomfort with weather changes. Severe or complicated fractures may result in persistent limitations requiring occupational adaptation. Mindfulness helps patients adapt psychologically to any residual limitations while celebrating recovered capabilities.
How does immobilization affect psychological well-being during recovery?
Forced immobility frequently triggers anxiety, depression, and identity disruption. Mindfulness practices prove particularly valuable during immobilization phases by providing purposeful mental activity, reducing catastrophic thinking, and transforming immobilization from a frustrating limitation into a meaningful healing ritual. Many patients report that mindfulness during immobilization significantly improves overall recovery experience.


