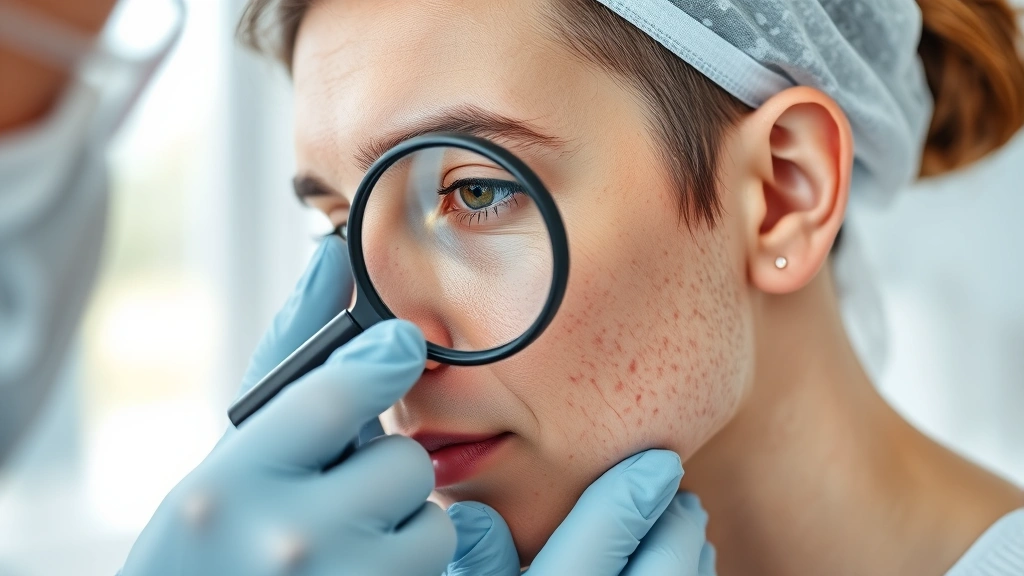

Is Oil Skin Therapy Effective? Dermatologists Weigh In
Oil skin therapy has become increasingly popular in recent years, with countless products and treatments promising to balance sebaceous gland activity and restore skin health. However, the question remains: does oil skin therapy actually work? Dermatologists and skincare experts have varying perspectives on this trending treatment approach, and understanding the science behind it is essential before investing time and money into these therapies.
The human skin naturally produces sebum, an oily substance that protects and moisturizes the epidermis. When sebum production becomes excessive, individuals develop oily skin characterized by enlarged pores, shine, and increased susceptibility to acne. Oil skin therapy aims to regulate this overproduction through various methods, from topical treatments to professional procedures. But separating fact from marketing hype requires examining clinical evidence and expert opinions.
Understanding Oily Skin: The Science Behind It
Oily skin results from the overactivity of sebaceous glands, which are distributed across the face, scalp, and upper back. These glands produce sebum, a naturally occurring lipid that serves critical protective functions. However, genetic predisposition, hormonal fluctuations, environmental factors, and certain medications can trigger excessive sebum production, leading to the characteristic shine and congestion associated with oily skin.
The sebaceous gland’s activity is primarily regulated by androgens, hormones that stimulate sebum secretion. This explains why oily skin often worsens during puberty and why individuals with hormonal imbalances frequently experience increased oil production. Additionally, external factors such as humidity, stress, and improper skincare routines can exacerbate the condition. Understanding these underlying mechanisms is crucial for evaluating whether oil skin therapy can effectively address the root causes or merely manage symptoms.
Dermatologists recognize that oily skin is not inherently problematic—in fact, adequate sebum production is necessary for healthy skin. The challenge lies in maintaining balance. When sebum production exceeds the skin’s natural capacity to regulate itself, it creates an environment conducive to bacterial growth, inflammation, and acne formation. This is where oil skin therapy interventions come into play, attempting to restore equilibrium without stripping the skin of essential protective oils.
Types of Oil Skin Therapy Treatments
Oil skin therapy encompasses a diverse range of treatments, each operating on different principles. Understanding these options helps consumers and patients make informed decisions about which approach might suit their specific needs.
Topical Oil Skin Therapy Products: These include cleansers, toners, serums, and moisturizers specifically formulated to regulate sebum production. Many contain ingredients like salicylic acid, niacinamide, zinc, or clay that help absorb excess oil and refine pores. Red light therapy near me represents an alternative approach gaining traction in professional settings.
Professional Procedures: Dermatologists offer several in-office treatments designed to manage oily skin. These include chemical peels, microdermabrasion, laser therapy, and specialized facials. Some clinics utilize advanced technologies like sebum-regulating devices that use radiofrequency or light-based energy to temporarily reduce oil production.
Oral Medications: For severe cases, dermatologists may prescribe oral medications such as isotretinoin (Accutane) or hormonal contraceptives that address the hormonal factors driving sebum production. These represent more aggressive interventions reserved for cases where topical and professional treatments prove insufficient.
Lifestyle and Dietary Modifications: Some oil skin therapy approaches emphasize lifestyle changes, including dietary adjustments, stress management, and proper hydration. The theory suggests that certain foods and stress levels influence hormonal balance and consequently sebum production.
What Dermatologists Say About Effectiveness
Dermatological consensus on oil skin therapy effectiveness is nuanced. Most board-certified dermatologists acknowledge that certain treatments can meaningfully reduce oily skin symptoms, but effectiveness varies considerably based on individual factors and treatment selection.
Dr. research from major dermatological institutions indicates that topical treatments containing niacinamide and salicylic acid demonstrate measurable effectiveness in reducing sebum production and improving skin texture. According to studies published in peer-reviewed journals, niacinamide can reduce sebaceous gland activity and decrease sebum excretion rates by approximately 25-30% with consistent use over 8-12 weeks.
Professional procedures receive more cautious endorsement from dermatologists. While chemical peels and laser treatments can provide temporary improvement, dermatologists often note that results are not permanent. The skin eventually returns to its baseline sebum production levels, requiring ongoing maintenance treatments. This reality underscores an important distinction: oil skin therapy can manage symptoms effectively but may not provide permanent solutions unless underlying hormonal or genetic factors are addressed.
Renowned dermatological organizations emphasize that the most effective approach typically combines multiple strategies. Rather than relying on a single treatment, dermatologists recommend integrating appropriate cleansing routines, targeted topical products, professional treatments when necessary, and lifestyle modifications. This comprehensive approach addresses both the symptoms and potential underlying causes of oily skin.
However, dermatologists also caution against over-treating oily skin. Aggressive oil removal can trigger a compensatory increase in sebum production, paradoxically worsening the condition. This counterintuitive response underscores why professional guidance is valuable when selecting oil skin therapy approaches.
Clinical Evidence and Research Findings
Scientific evidence supporting oil skin therapy effectiveness comes from numerous clinical trials and dermatological research studies. Research published through the National Center for Biotechnology Information documents the efficacy of various treatment modalities for sebaceous gland regulation.
A landmark study examining salicylic acid’s effects on oily skin found that 2% salicylic acid solutions applied twice daily reduced comedone formation by 35% and decreased overall oiliness scores by 40% over a 12-week period. Similarly, dermatological journals have published multiple investigations confirming niacinamide’s sebum-regulating properties through different mechanisms than salicylic acid, suggesting potential synergistic benefits when combined.
Laser and light-based therapies show promise in clinical settings. Studies examining fractional laser treatments and intense pulsed light (IPL) therapy indicate temporary but significant reductions in sebum production. However, these benefits typically persist for 2-6 months, after which sebaceous gland activity returns to baseline levels. This temporary nature necessitates periodic retreatment for sustained results.
Research into oral medications reveals that isotretinoin produces the most dramatic and longest-lasting results for severe oily skin and acne. PubMed databases contain extensive documentation of isotretinoin’s ability to permanently reduce sebaceous gland size and sebum production. However, the medication’s significant side effect profile limits its use to severe cases where other treatments have failed.
Interestingly, recent research has explored the role of proper hydration and balanced skincare in oil skin management. Studies suggest that dehydrated skin often overcompensates by producing excess sebum, making adequate moisturization paradoxically beneficial for oily skin types. This finding has shifted some dermatological recommendations toward more balanced, hydrating oil skin therapy approaches rather than harsh, drying regimens.
Natural vs. Professional Oil Skin Therapy
The debate between natural remedies and professional oil skin therapy treatments reflects broader skincare philosophy differences. Natural approaches typically employ ingredients like tea tree oil, witch hazel, clay masks, and botanical extracts. While these substances possess antimicrobial and astringent properties, clinical evidence supporting their efficacy in regulating sebum production remains limited compared to scientifically formulated products.
Tea tree oil demonstrates mild antimicrobial activity that may help prevent acne-causing bacteria colonization on oily skin. However, studies show its sebum-regulating properties are modest compared to established ingredients like salicylic acid or niacinamide. Clay masks can absorb surface oil temporarily, but this effect is superficial and short-lived, typically lasting only hours after application.
Professional oil skin therapy treatments, by contrast, target sebaceous gland function at deeper biological levels. Chemical peels penetrate the epidermis, stimulating cellular turnover and temporarily reducing sebum accumulation. Laser treatments can ablate sebaceous gland tissue or modulate their activity through thermal and photochemical mechanisms. These approaches produce measurable, sustained improvements documented through clinical metrics.
That said, many dermatologists recognize value in combining natural and professional approaches. Gentle natural ingredients may support skin health and comfort while professional treatments address the underlying physiological factors driving excessive oil production. This integrative strategy respects both traditional skincare wisdom and modern scientific evidence.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
While oil skin therapy is generally considered safe, certain treatments carry specific risks that patients should understand before proceeding. Topical treatments containing salicylic acid or retinoids can cause irritation, dryness, redness, and peeling, particularly during initial use or in sensitive individuals. These side effects typically diminish as skin acclimates, but they can be uncomfortable during the adaptation period.
Professional procedures pose more significant risks. Chemical peels can cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, particularly in individuals with darker skin tones. Laser treatments carry risks of burns, scarring, and temporary or permanent color changes in treated skin. Infections, though rare, are possible complications following any invasive procedure. Oral medications like isotretinoin carry substantial risks including severe birth defects, depression, and liver function abnormalities, necessitating rigorous monitoring during treatment.
Additionally, some individuals experience the “rebound effect” where aggressive oil removal triggers compensatory sebum overproduction, temporarily worsening oiliness. This underscores the importance of gradual treatment introduction and professional guidance. Understanding these risks helps patients make informed decisions and select treatments appropriate for their risk tolerance and skin sensitivity.
Combining Oil Skin Therapy with Other Treatments
The most effective oil skin therapy approaches often involve combining multiple complementary treatments. For instance, integrating occupational therapy masters programs principles of holistic wellness with dermatological treatment can support overall skin health through stress management and lifestyle optimization. Similarly, understanding therapeutic approaches to wellness can inform broader health perspectives that indirectly support skin healing.
A comprehensive oil skin therapy regimen might include: a gentle cleanser twice daily, a niacinamide-containing serum, a lightweight non-comedogenic moisturizer, weekly clay masks, monthly professional facials or chemical peels, and dietary modifications emphasizing anti-inflammatory foods and adequate hydration. This multi-pronged approach addresses oil production through topical regulation, professional intervention, and systemic health optimization.
Dermatologists increasingly recommend combining topical treatments with behavioral modifications. For example, reducing stress through meditation or exercise, maintaining consistent sleep schedules, and avoiding pore-clogging cosmetics can amplify the benefits of medical treatments. This synergistic approach recognizes that skin health depends on both external interventions and internal physiological balance.
Some patients benefit from combining oil skin therapy with massage therapy jobs near me concepts, as professional massage can reduce stress hormones and improve circulation, indirectly supporting skin health. While massage itself doesn’t directly regulate sebum, its stress-reduction benefits may help address hormonal contributors to oily skin.
FAQ
How long does it take for oil skin therapy to show results?
Results vary depending on the treatment type. Topical products typically require 4-8 weeks of consistent use before noticeable improvement occurs. Professional procedures may show immediate effects, though full results develop over 2-4 weeks as skin heals and remodels. Oral medications like isotretinoin require 4-6 months for maximum benefits.
Can oil skin therapy cure oily skin permanently?
Most oil skin therapy approaches manage symptoms rather than provide permanent cures. Only isotretinoin, which permanently reduces sebaceous gland size, offers long-lasting results. Other treatments provide temporary to medium-term improvements that typically last months to a year before retreatment becomes necessary.
Is oil skin therapy suitable for sensitive skin?
Many oil skin therapy products and procedures can be adapted for sensitive skin. Gentle formulations with lower concentrations of active ingredients, milder professional treatments, and slower introduction schedules allow sensitive-skinned individuals to benefit from oil skin therapy. Professional dermatological guidance is particularly important for this population.
Can diet affect oil skin therapy effectiveness?
Yes, research increasingly supports diet’s influence on sebum production. High-glycemic foods and dairy products may exacerbate oiliness in some individuals. Conversely, anti-inflammatory foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants may support treatment effectiveness. A balanced, whole-food-focused diet can enhance oil skin therapy results.
Are there age-related considerations for oil skin therapy?
Oil skin is most common during adolescence and early adulthood when hormonal activity peaks. However, oily skin can persist into adulthood and even develop later in life due to hormonal changes or other factors. Oil skin therapy approaches can be adapted across age groups, though treatment selection should consider age-related skin characteristics and healing capacity.
What’s the difference between oily skin and combination skin regarding therapy?
Combination skin features oily zones (typically the T-zone) alongside normal or dry areas. Oil skin therapy for combination skin requires more targeted approaches using different products in different zones. Professional treatments can also be localized to oily areas, making combination skin management more nuanced than treating uniformly oily skin.
How does oil skin therapy compare to how much is therapy for other conditions?
Dermatological oil skin therapy costs vary considerably. Topical products range from $15-100 monthly, professional procedures cost $150-500 per session, and oral medications may require significant out-of-pocket expenses depending on insurance coverage. Understanding these costs helps patients select sustainable treatment approaches aligned with their budgets.


